Substrates are individual glass plies used to process the final product, also known as float glass, raw glass or monolithic glass.
Substrates are available in colorless, low iron or colored appearance, and different thickness options.
Colorless is a glass substrate with a slight green tint. Low iron is a substrate with lower iron content in its mass, which reduces the green tone and increases transparency.
There are many options for colored glass. In addition to providing a specific appearance, colors have the benefit of improving performance.
Colors
| Clear | Green | Gray | Dark Green | Bronze | Blue | Extra-clear(low iron) |
|---|
All substrates are available in 4mm and 6mm.
For other thickness options, please contact our sales or specification department.
Special Substrates
Anti-reflective glass
Anti-reflective glass is produced by applying coating that attenuates unwanted light reflectance, not changing the product’s transparency. Those are optimal for places demanding low reflection, such as shop windows and libraries.
Self-cleaning glass
A clear coating applied to the glass acts as a “repellent” of dirt, water and other liquids, which renders the building’s maintenance easier.
The self-cleaning properties are activated by sunlight; therefore, it is recommended for use in facades and roofs.
Substrate Location
Parts with multiple layers of glass must have their substrate to be used in each layer duly specified, because their location is directly related to performance.
Insulating Glass
6mm Coating Glass with substrate Green #2
+ 12mm airspace + 6mm Clear
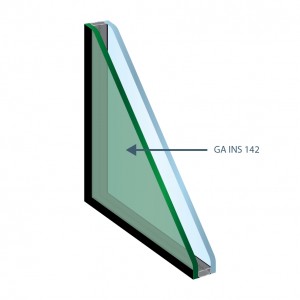
TL: 41%
RLe: 19%
Abs: 66%
FS: 26%
Valor U: 1,6 W/(m².K)
6mm Coating Glass #2 + 12mm airspace
+ 6mm Green
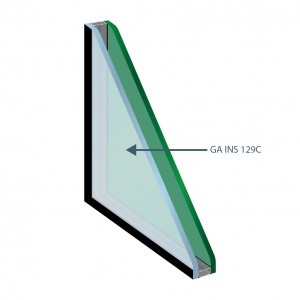
TL: 41%
RLe: 25%
Abs: 48%
FS: 34%
Valor U: 1,6 W/(m².K)
Laminated Glass
6mm Coating Glass with substrate Green #2
+ 0.38mm Clear PVB + 6mm Clear
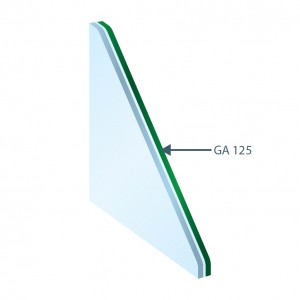
TL: 38%
RLe: 9%
Abs: 73%
FS: 37%
Valor U: 5,5 W/(m².K)
6mm Coating Glass #2 + 0.38mm
Clear PVB + 6mm Green
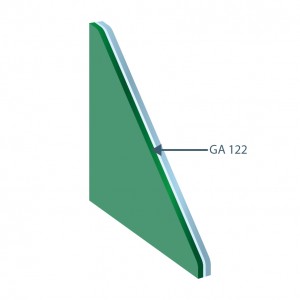
TL: 39%
RLe: 16%
Abs: 59%
FS: 34%
Valor U: 5,6 W/(m².K)
Coating is a thin layer of metal applied to the glass to improve its energy performance. It is also known as solar control glass.
The first generation of coatings was a reflective layer, which would give buildings a mirrored appearance. Due to its high sunlight reflectance and absorption capacity, reflective glass reduces heat and provides thermal comfort and less intense light transmittance.
More recently, the use of low-emissivity (low-e) coatings has increased in urban landscapes. Due to its ability to reflect long-wave infrared radiation, the low-e coating further reduces heat absorption, resulting in greater energy savings for the building.
Reflective and low-e glass can be manufactured through online or offline processes, also known as pyrolytic and sputtering processes, respectively.
The former involves a thin metal layer that is applied during the manufacturing process of float glass. In turn, the off-line process involves the application of multiple coating layers within a vacuum chamber.
The reflective and e-low glass processed by GlassecViracon meet the NBR 16015 standard requirements.
Coating Face Position
The position of the coated product follows the recommended designations for surfaces, also called faces.
Each glass part has two faces. The face facing the exterior of the building is called face #1; the back of this part is called face #2.
For glass with multiple glass parts, each of them has a name, according to the examples below.
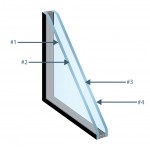
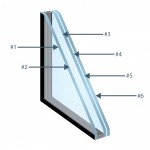
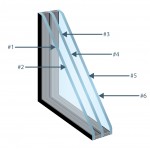
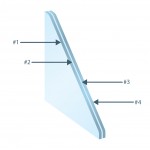
Spandrel is the panel located between the vision area and the area covering the structural columns, floors and walls. For this type of application, GlassecViracon offers silk-screened glass alternatives.
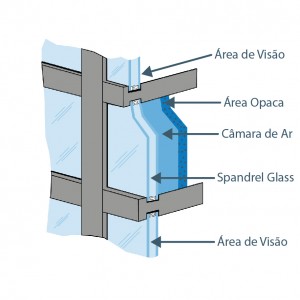
Harmonizing Spandrel and the Vision Area
Design in general requires that the spandrel (blind spot) glass be harmonized with the glass in the building’s vision areas.
However, this can be a difficult task when glass has high light transmittance and low external reflectance — that is, when the glass is more transparent.
For these cases, low light transmittance glass combined with high reflectance glass offer the lowest contrast between the blind spot and the vision areas, regardless of varying light conditions.
In addition, changing sky conditions can also influence our perception of the glass color and its overall appearance.
On a clear, sunny day, the intensity of the light outside is approximately 50 to 100 times higher than in the lighted interior of a building.
When glass is seen from outside the building, the dominant visual characteristic is that of external reflection. On cloudy days, there is greater visual disparity between the blind spot and the vision area.
This effect is due to the transparency of the glass and the depth perception created by the interior lighting. Blind spot areas tend to have a flat appearance with only two dimensions by contrast.
The glass used in blind spots is opaque because it can only be seen by reflection.
The glass used in blind spots is opaque because it can only be seen by reflection. As light transmittance from the glass vision area increases when weather is cloudy, the interior light becomes predominant.
GlassecViracon recommends that an analysis of samples or full-size prototypes be made of the glass to be used for harmonization between the vision area and the blind spot when the light transmittance of the glass vision area exceeds 14%.
A greater contrast between the vision area and the blind spot occurs when uncoated, colored (green, bronze, blue, etc.) or high light transmittance glass is used.
Under these conditions, insulating units in the blind spot can create the illusion of depth and more accurately resemble the glass in the vision area.
By building the vision area and the blind spot in a similar manner (the same color as external glass, coating, among other aspects), contrast can be minimized according to lighting conditions.
In order to specify your silk-screened product, it is important to select the pattern, color and orientation of the figure on the face where it will be applied. If you choose to create your own design, send us a high resolution dwg, and our team will develop your product.
Silk-screen Standards
- 20% cover
- 30% cover
- 50% cover
- 60% cover

Full Silk-screen
In full silk-screen, ceramic ink is applied to the entire face of the part, in the reference colors of the RAL system. This technique is widely used in spandrel glass and wall coating.
Silk-screen
Due to its great versatility, silk-screened glass is widely used in roofs and facades to meet energy performance, design and coating requirements.
GlassecViracon’s silk-screened glass is heat-treated and may be heat-strengthened or tempered to offer superior thermal and mechanical resistance as a monolithic glass with the same thickness, type and size.
In order to specify your silk-screened product, it is important to select the pattern, color and orientation of the figure on the face where it will be applied. If you choose to create your own design, send us a high resolution dwg, and our team will develop your product.


Moiré Effect
The Moiré effect is an optical phenomenon that presents itself in wavy, crimped or circular shapes under certain conditions.
It is a pattern formed when two regularly spaced designs are overlaid but not aligned.
Common examples of this effect are window screens or braided fabric. In this case, the Moiré standard seems “waiving” when light is reflected from the surface.
Thermal treatment is the process through which glass goes in a tempering furnace in order to change its characteristics of resistance to thermal and mechanical variations. This process reinforces the float glass properties, causing it to have breakage patterns that are appropriate to applications in safety glazing. GlassecViracon provides two types of glass issued from the thermal treatment processes: heat-strengthened and tempered glass. For thermal treatment of solar control glass, GlassecViracon recommends a minimum thickness of 6 mm.
Heat-strengthened glass
It is twice as strong as float glass of the same thickness and size. If broken, the heat-strengthened glass fragments will present different characteristics that will be adhered by the bonding system, not detaching from the gap.
This type of glass is heat treated and when properly processed must have residual surface tension between 3,500 psi and 7,500 psi to meet the ASTM C 1048 and NBR 16918:2020 standards for heat-strengthened glass.
Tempered glass
It is between four and five times stronger than float glass and two and a half times stronger than heat-strengthened glass of the same thickness and size.
If broken, the tempered glass forms small, relatively harmless pieces, reducing the chance of injury.
This type of glass is heat treated and when properly processed must have residual surface tension between 10,000 psi or edge compression equal to or above 9,700 psi, and that meets the NBR 14698:2001 or NBR 7199:2016 construction glazing standards.
Heat Soak Test
HST is a thermal treatment complementary to tempering designed to eliminate glass that have nickel sulfide particles in its mass, which causes the so-called spontaneous breakage.
Such particles are invisible and therefore not detectable during the manufacturing process.
In the HST process, tempered glass is heated to 260oC and remains at that temperature for two hours. If present, nickel sulfide particles expand due to temperature variation, causing the glass to spontaneously break inside the equipment.
This test significantly reduces the risk of spontaneous breakage of tempered glass after installation, thus avoiding accidents, replacement costs and other inconveniences, such as interdiction of the surroundings and situations of panic, stress and insecurity of users.
Heat-strengthened glass will not be subject to spontaneous breakage due to a lower degree of compression of its surface. Thus, tensions are not sufficient for the expansion of the nickel sulfide to cause the glass to break.

GlassecViracon offers options of holes and cuts to customize your product.
With a state-of-the-art machining center capable of producing extra-large parts, holes and cuts in our glasses have greater precision and a perfect finish.
Below you will find the cut patterns provided by GlassecViracon.
If you want a special model, please contact our team.
90 DEGREE ANGLE PROFILE
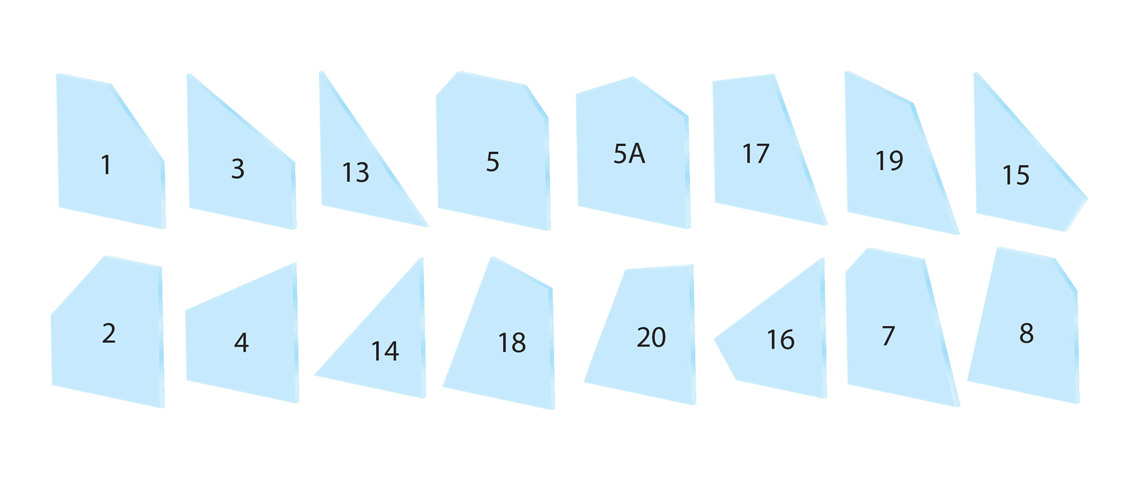
PROFILES WITHOUT 90-DEGREE ANGLE
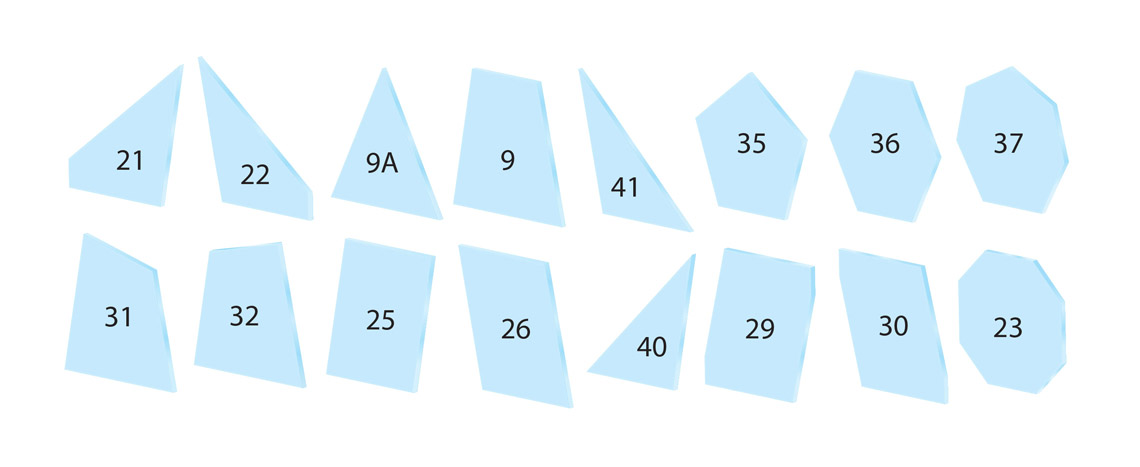
RADIUS PROFILE
OTHER PROFILES
Seamed, ground or polished edges. These are the three types of finish provided by GlassecViracon.
For special finishing, contact our team .

